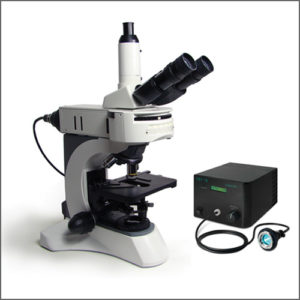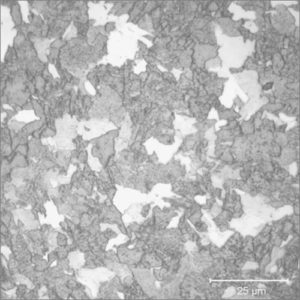


Metallographic Microscope
Metallographic (metallurgical) microscope is used to study of the physical structure and components of metals and alloys.
- Description
| Testing Method | Metallographic Microscope |
| Description | Metallography or metallurgy is the study of the structure of metals and alloys. Metallographic microscope can be used as a tool to help identify a metal or alloy, to determine whether an alloy was processed correctly, to examine multiple phases within a material, to locate and characterize imperfections such as voids or impurities, or to observe damaged or degraded areas in failure analysis investigations. In short, metallographic microscope can reveal a great deal about the past history of a metal specimen, and how it will act in service. |
| More Information | Wikipedia: Metallography |
Related Products
-
Shaking Incubator
Shaking incubator is often used for cell culturing, cell aeration, and solubility studies.
-
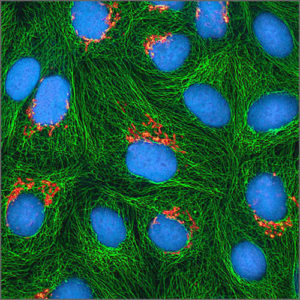
Fluorescence Microscope
Fluorescence microscope uses fluorescence and phosphorescence to study properties of organic or inorganic substances.
-
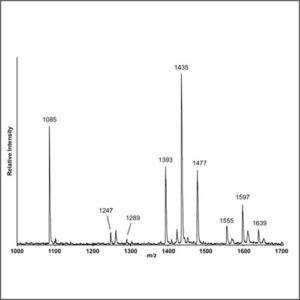
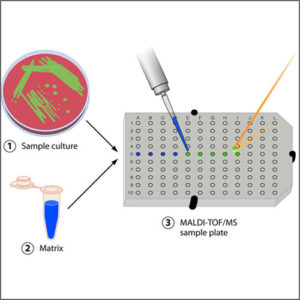
Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS)
Mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) is an analytical technique that ionizes chemical species and sorts the ions based on their mass to charge ratio.
-
UV-Vis-NIR Spectroscopy
UV-Vis-NIR spectroscopy is routinely used in analytical chemistry for the quantitative determination of various analytes, such as transition metal ions, organic compounds, and biological macromolecules.
-
Size Exclusion Chromatography (GPC/GFC)
Size-exclusion chromatography is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size or by their molecular weight.