Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM + EDX)
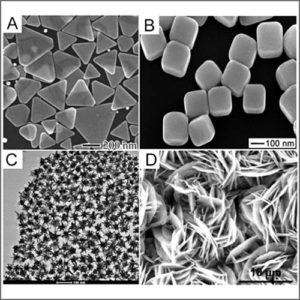
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is a non-destructive technique that uses an electron beam probe to analyse surface details down to nano-scale, and to produce high magnification images with high resolution.
- Description
| Testing Method | Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM + EDX) |
| Description | Scanning electron microscope (SEM) is a type of electron microscope that produces images of a sample by scanning it with a focused beam of electrons. The electrons interact with atoms in the sample, producing various signals that contain information about the sample’s surface topography and composition.
The most common SEM mode is detection of secondary electrons emitted by atoms when excited by the electron beam. By scanning the sample and collecting the secondary electrons that are emitted using a special detector, a high-resolution image displaying the topography of the surface is created.
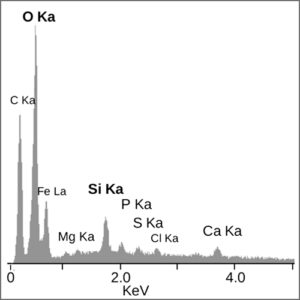
Characteristic X-rays that are produced by the interaction of electrons with the sample may also be detected in an SEM equipped for energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). Analysis of the x-ray signals is used to identify the composition and measure the abundance of elements in the sample.
SEM has a variety of applications in a number of scientific and industry-related fields, especially where surface characterizations of solid materials are beneficial.
(1) SEM is an essential tool for materials science and engineering. The development of nanotechnology is heavily dependent on the application of SEM.
(2) In life sciences and research, SEM has become an integral technology. Recent development of biocompatible materials, tissue engineering research, microbiology and many have close relationship with SEM imaging technique.
(3) SEM, in combination with focus ion beams (FIB), is an ideal technique in semiconductor industry by offering analytical capabilities with high levels of precision.
(4) Equipped with an Energy Dispersion X-ray analyzer (EDX), SEM can reveal spatial variation in chemical composition, provide qualitative chemical analysis and identify crystalline structure of samples. |
| More Information | Wikipedia: Scanning Electron Microscope |